Research Report Title: Investigating the use of DL and AI in medical image analysis for aiding diagnosis
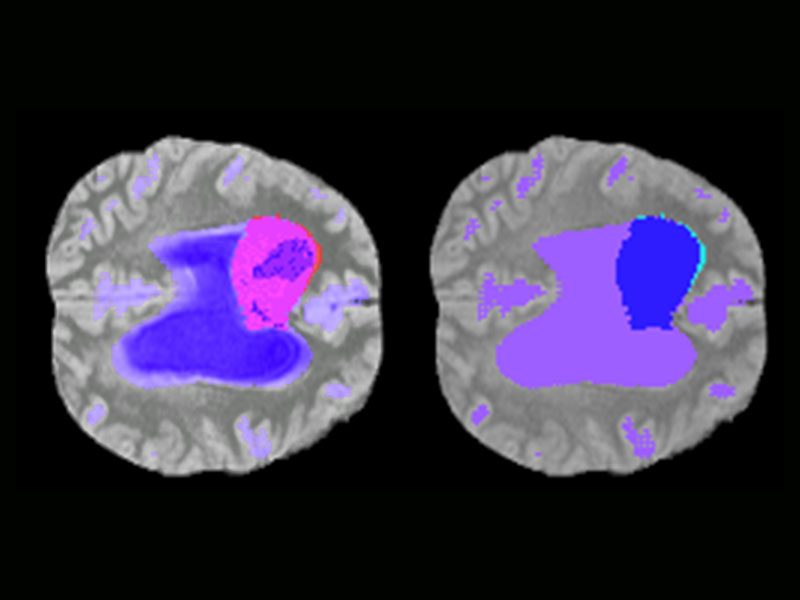
As part of my Honours Degree project at Abertay University, I completed a research project which involved investigating the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for segmenting brain tumours in MRI volumes. With supervision from Salma ElSayed, I systematically researched, designed, developed, and evaluated an AI pipeline for anomaly segmentation. Both quantitative and qualitative results were gathered an evaluated. Among the set of qualitative results, 8 responses were gathered from a range of radiographers, student doctors, and MRI technologists. Due to the pandemic limiting access to suitable compute power, results were limited in train time which as a result meant that models did not fully converge within the time-scales of the project. Regardless of this, significant research and development was employed to produce and communicate the findings of the research.
The context from the report is as follows:
Early diagnosis of cancerous tumours yields life-changing impact on patient survival. Tools and technologies can be developed to harness the vast amount of data hidden within MRI scans which in turn can influence and promote early detection of tumours.
The aim of the project is to identify the effectiveness of deep learning algorithms in identifying anomalies/abnormalities in brain scans and evaluate to what extent this may influence patient diagnosis.
A deep learning prototype system was developed which is capable of detecting the presence of tumours in MRI brain scans to a certain degree. Quantitative data results of accuracy will allow for evaluation of effectiveness while qualitative data gathering allows for an opinion-based response from highly trained personnel. Quantitative data can then be compared to that of studies in this field along with comparisons to typical unaided patient diagnosis statistics by doctors. Qualitative data was used to find additional angles in which the system could be improves and addressed important factors when considering the implementation of the prototype in a clinical setting.
This project seeks to enhance the decision-making process of doctors and radiologists by developing a tool which can aid them in finding anomalies within MRI scans. An evaluation of effectiveness will be drawn from the quantitative and qualitative results.
The findings of this paper illustrate how artificial intelligence can be used as a decision-making aid to better help diagnose patients and reduce false negatives